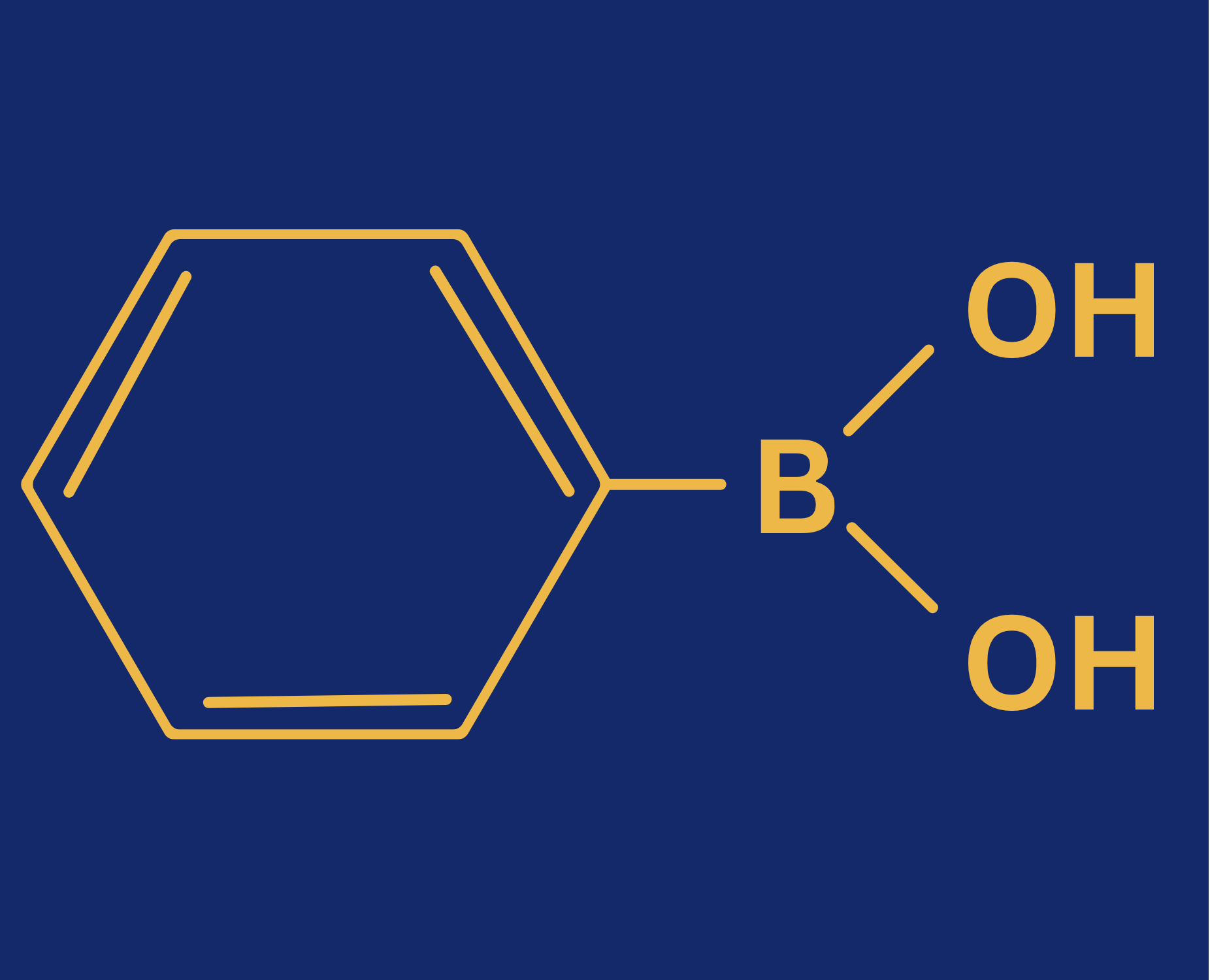
Phenyl Boronic Acid (PBA)
Specifications of Phenyl Boronic Acid
- Purity : 98.00% – 99.50%
Melting Range : 215-220°C
Physical & Chemical Properties
| CAS Number | 98-80-6 |
| Molecular Formula | C6H7BO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 1121.93 g/mol |
| Appearance | White Powder |
| Density | 1.13 g/cm³ |
| Flash Point | 114.6°C |
| Refractive Index | 1.534 |
Applications of Phenyl Boronic Acid
- It is extensively used in Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reactions, enabling the efficient synthesis of biaryl structures, which form the backbone of numerous active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and advanced organic molecules.
In the healthcare and diagnostic sector, phenylboronic acid is valued for its ability to reversibly bind cis-diols, making it an excellent candidate for glucose-sensing technologies such as biosensors, contact lenses, and diagnostic assays.
In materials science, phenylboronic acid contributes to the creation of smart polymers and hydrogels. These materials respond dynamically to stimuli like pH or glucose concentration, finding use in drug delivery systems, insulin-releasing hydrogels, and wound healing materials.
its reactivity allows for surface modification and functionalization in nanotechnology and advanced materials, enhancing the design of sensors, coatings, and biomedical interfaces.
Advantages of Phenyl Boronic Acid
- It is widely used in palladium-catalyzed Suzuki coupling reactions for efficient carbon-carbon bond formation in organic synthesis.
- As a mild Lewis acid, it is generally stable, easy to handle, and less toxic compared to other organometallic reagents used in similar chemical reactions.
Packing:
- 30 kg HDPE drum
- Small Glass Plastic Bottle
Shipping Regulation
| H.S. Code | 29319090 |



